

Multi-slice temporal CT data were obtained from 80-row and 320-row detector CT (Canon Medical Systems, Tochigi, Japan). Anatomical structures were evaluated using the temporal bone CT. All patients provided informed consent, and the study protocol was reviewed and approved by the relevant Institutional Review Board (Approval No.

This study examined 32 patients (60 ears) diagnosed with chronic perforated otitis media and 30 patients (60 ears) that underwent temporal bone computed tomography (CT) owing to symptoms such as sensorineural hearing loss, facial paralysis, and dizziness, at the Shonan Kamakura General Hospital from April 2019 to March 2022.Ĭhildren under the age of 18 years, patients with trauma, congenital malformations, auditory canal cholesteatoma, and acquired cholesteatoma, and non-Asian cases were excluded because in these cases the EAC morphology may have been affected for other reasons. In this study, we investigated these anatomical structural relationships to predict the morphology of the vital structures in the middle ear based on the EAC morphology. However, there have been no reports examining these relationships. If the morphology of the tympanic sinus, which is a difficult-to-operate area in the middle ear, and the morphology of the vertical portion of the facial nerve and the jugular bulb, which are prone to collateral damage, can be inferred from the morphology of the EAC, it would be useful for the prediction of the morphology of the middle ear during the medical examination. In such instances, it is necessary to exercise caution to prevent damage to important structures. The introduction of endoscopes in recent years has made it possible to obtain a clear field of view even in cases of EAC curvature however, sometimes it may be necessary to shave the EAC bone in order to perform sufficient operations. There are individual variations in the morphology of the EAC, and these differences limit the ease of inspection and the range of possible operations. The morphology of the external auditory canal (EAC) is the first structure to be visually confirmed in the diagnosis of ear diseases moreover, middle ear diseases are often surgically treated via the EAC.
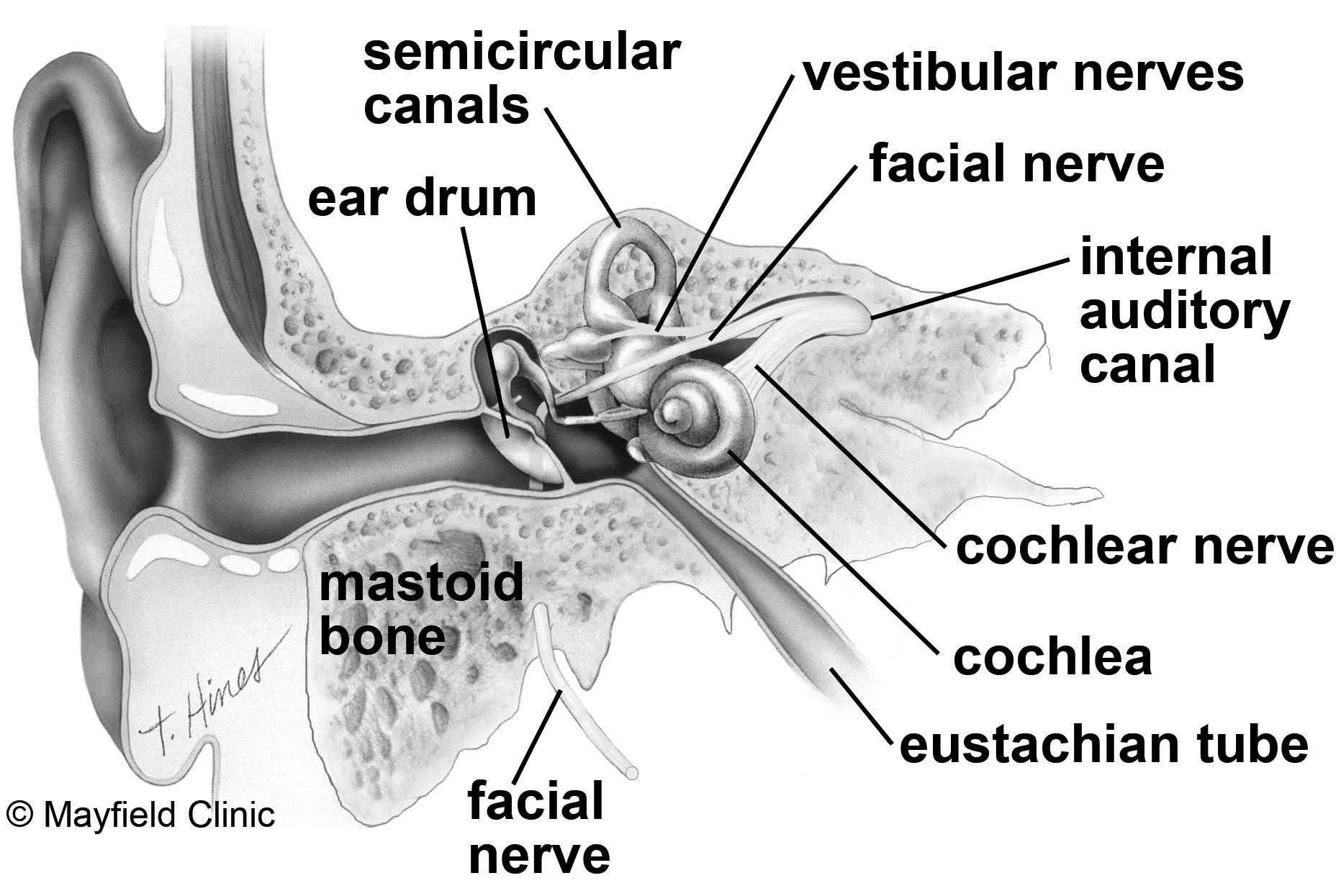
These findings aid in predicting the difficulty of tympanic sinus operation and reducing facial nerve damage risk during EAC excision. ConclusionĪ severe overhang of the inferior wall of the EAC and short antero-posterior length of the bony tympanic ring indicates a higher possibility of a shallow tympanic sinus and an outward orientation of the vertical portion of the facial nerve. The EAC morphology correlated with the tympanic sinus depth and outward orientation of the vertical portion of the facial nerve. Furthermore, the tympanic sinus was shallow, and vertical portion of the facial nerve tended to run outward. In ears with chronic otitis media, the overhang of the inferior wall of the EAC was significantly more than that in normal ears, and the antero-posterior length of the bony tympanic ring was short. The anatomical morphology of the EAC, tympanic sinus, vertical portion of the facial nerve, and jugular bulb were measured, and the anatomical relationship between the EAC morphology and important structures of the middle ear was analyzed. Temporal bone CT from 62 patients (120 ears) was used to perform 3D reconstruction (maximum intensity projection), of which 32 patients (60 ears) had chronic otitis media and 30 patients (60 ears) had normal temporal bones. We aimed to evaluate the morphology of the external auditory canal (EAC) using a three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of computed tomography (CT) scans of the temporal bone to corroborate and predict important anatomical structures involved in middle ear surgery based on the EAC morphology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
